Maternal and Newborn Health Study

The PRISMA Maternal and Newborn Health study is a prospective, open cohort study with a planned recruitment of about 20,000 pregnant women over three years across six research sites in two South Asian and three sub-Saharan African countries. Participants are pregnant women identified through active house-to-house and facility-based surveillance at less than 20 weeks gestation, as determined by ultrasound. High-quality data will be collected over 12 study visits: five antenatal care (ANC) visits, labor and delivery, and six postnatal care (PNC) visits up to one year postpartum. A total of 34 standardized maternal and fetal/infant outcomes will be assessed. The primary analysis will estimate the burden of adverse outcomes and examine the risk factors to inform potential intervention strategies. Data from this effort will also be used to develop normative values for pregnant and postpartum women, as well as predictive models to evaluate pregnancy risk.
Redefining Anemia in Pregnancy and Postpartum Study
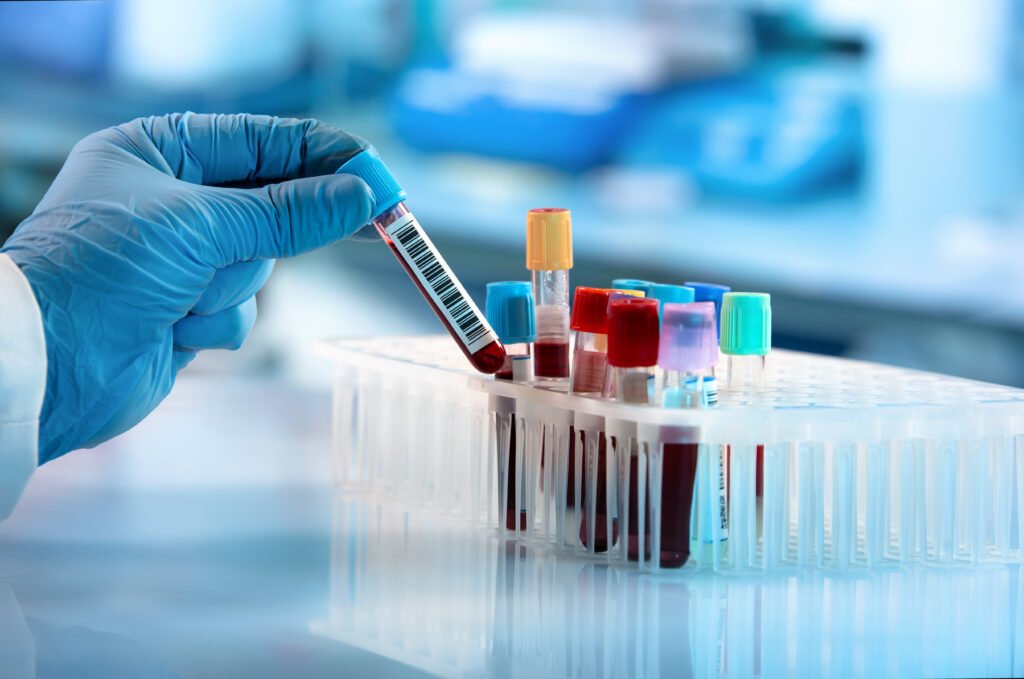
Redefining Maternal Anemia in Pregnancy and Postpartum (ReMAPP) is a multisite, prospective, open cohort study nested within the ongoing PRISMA Maternal and Newborn Health study. Participants are pregnant women who provide serial hemoglobin samples using gold standard methods at 20 weeks, 20 weeks, 28 weeks, and 36 weeks gestation and at six weeks and six months postpartum. We will use two analytical approaches to estimate hemoglobin thresholds: (1) clinical decision limits for gestational-age-specific anemia based on associations of hemoglobin levels with adverse maternal, fetal, and neonatal health outcomes and (2) reference limits for mild, moderate, and severe anemia based on tail statistical percentiles of hemoglobin values in a clinically healthy subpopulation. We also will conduct biomarker-intensive testing among a subset of participants in each trimester to explore underlying contributing factors of maternal anemia.
Bili-ruler Evaluation
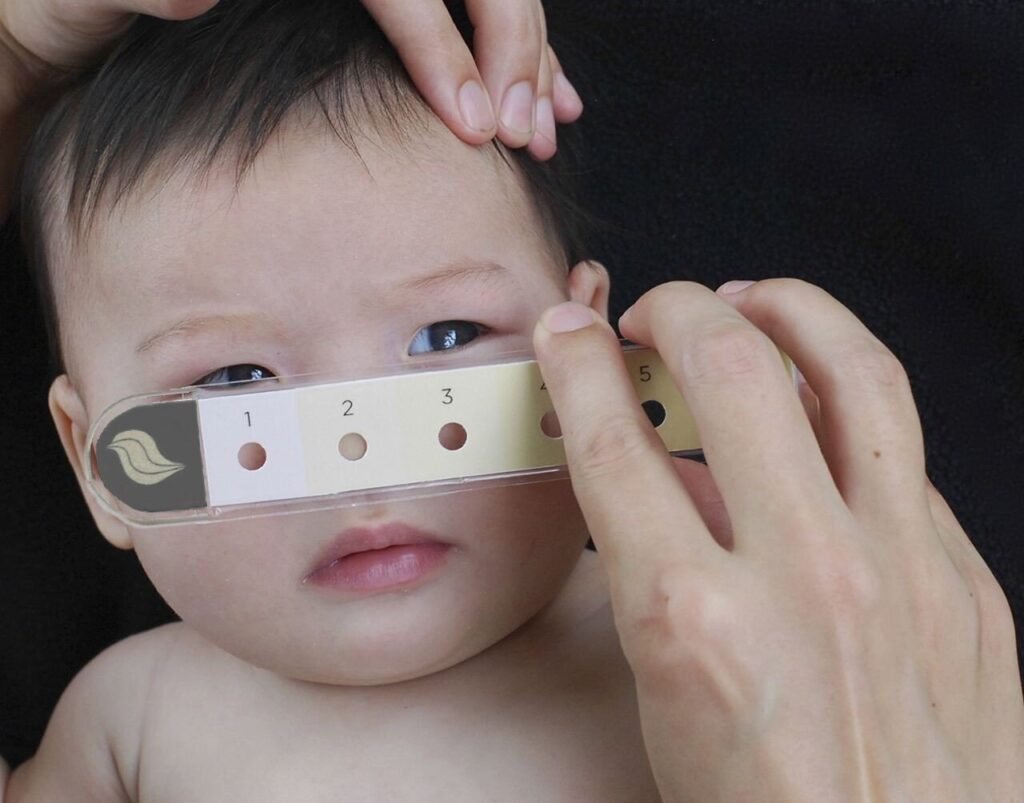
The Bili-ruler is a low-cost, easy-to-use plastic icterometer with six shades of yellow on an ordinal scale that could enable more accurate universal jaundice screening in diverse settings. This Bili-ruler evaluation is nested within the PRISMA Maternal and Newborn Health Study. Bilirubin will be assessed in newborns at 24 hours, 3 days, and 7 days postnatal. Bilirubin will be measured using visual inspection, Bili-ruler, and the BiliCare transcutaneous bilirubinometer. Skin tone will be assessed using the Monk Skin Tone Scale. The primary objectives are to assess the ability of Bili-ruler to identify significantly high bilirubin levels, as well as to assess the inter-rater agreement of Bili-ruler measurements taken by two users.
Continuous Non-invasive Hemoglobin Monitoring Device Validation Study
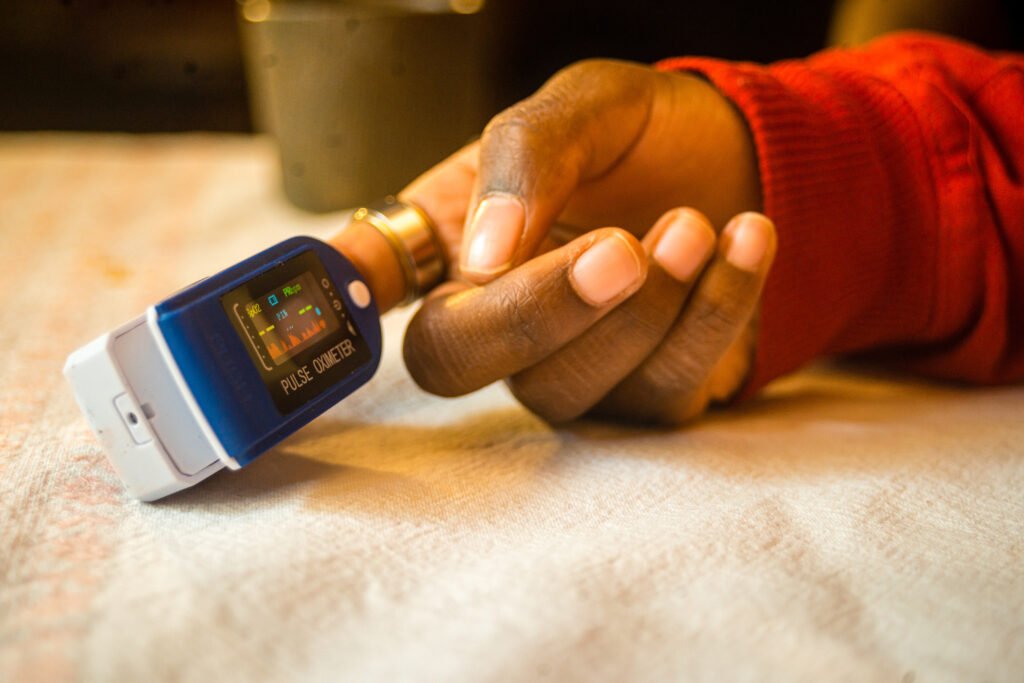

The Masimo Total Hemoglobin SpHb® is a continuous and non-invasive handheld device to measure hemoglobin levels. Previous research has found that SpHb is able to accurately detect hemoglobin levels in adult patients with a similar degree of bias and standard deviation to point-of-care invasive method measurements. Generally, limited clinical evidence, lack of validation of Masimo at higher than and lower than hemoglobin threshold values, and scientific consensus supporting the use of Masimo for accurate hemoglobin testing for the diagnosis of anemia during pregnancy calls for further research. We will measure hemoglobin using a venous blood sample via hematology auto-analyzer complete blood count (gold standard) and the non-invasive device to assess agreement.
Measuring Infant NeuroDevelopment Study
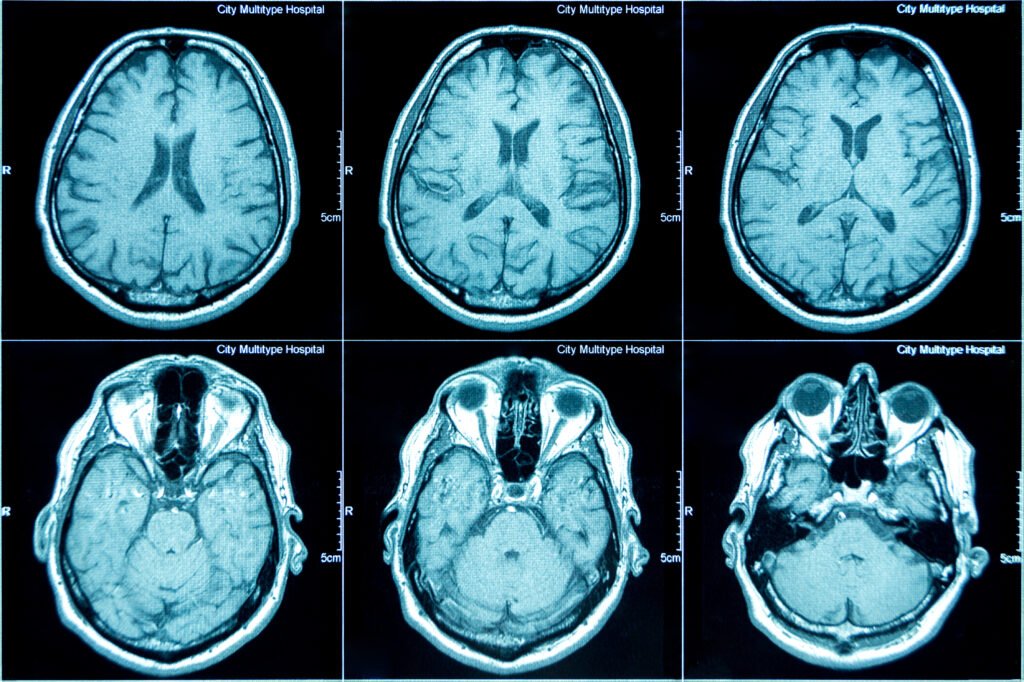
The ReMAPP Measuring Infant NeuroDevelopment (ReMIND) Study aims to advance clinical knowledge of the effects of maternal anemia on infant neurological development and brain morphology. Nested within the ReMAPP study, up to 300 mother-infant dyads will be selected to undergo neurodevelopmental assessments. Infant brain morphology will be assessed using the low-field, portable Hyperfine MRI done at 3 months and 1 year. The Global Scale for Early Development (GSED) Short-Form (SF), GSED Long Form (LF), & Family Care Indicator (FCI) assessments will be done at the same timepoints.
Bridging Global Gender Gaps in Disease Burden Estimation Study

The Bridging Global Gender Gaps (G3) in Disease Burden Estimation Study uses a mixed-methods, multi-phased approach to design a tool to capture how the symptoms of pregnancy and postpartum impact women’s health, functioning, and wellbeing. Without this, we cannot adequately measure the impact that maternal morbidities have on pregnant and postpartum women’s health-related quality of life. Globally, there is limited data that quantifies the number of women affected, leaving us unable to estimate the true burden of disease.
